
Procure to pay (P2P) is one of the most desired areas of audit for any organisation considering the complexity involved in procurement process and the huge cash flows. The possibility of leaking cash in this area is quite high and it remains easier for the perpetrators to commit fraudulent activities.
It is important to understand the organisation policies & procedures, the organisation structure and during the walkthrough understand the design of the processes. Here’s a simple look at the process involved in P2P (Also most commonly asked Interview question)
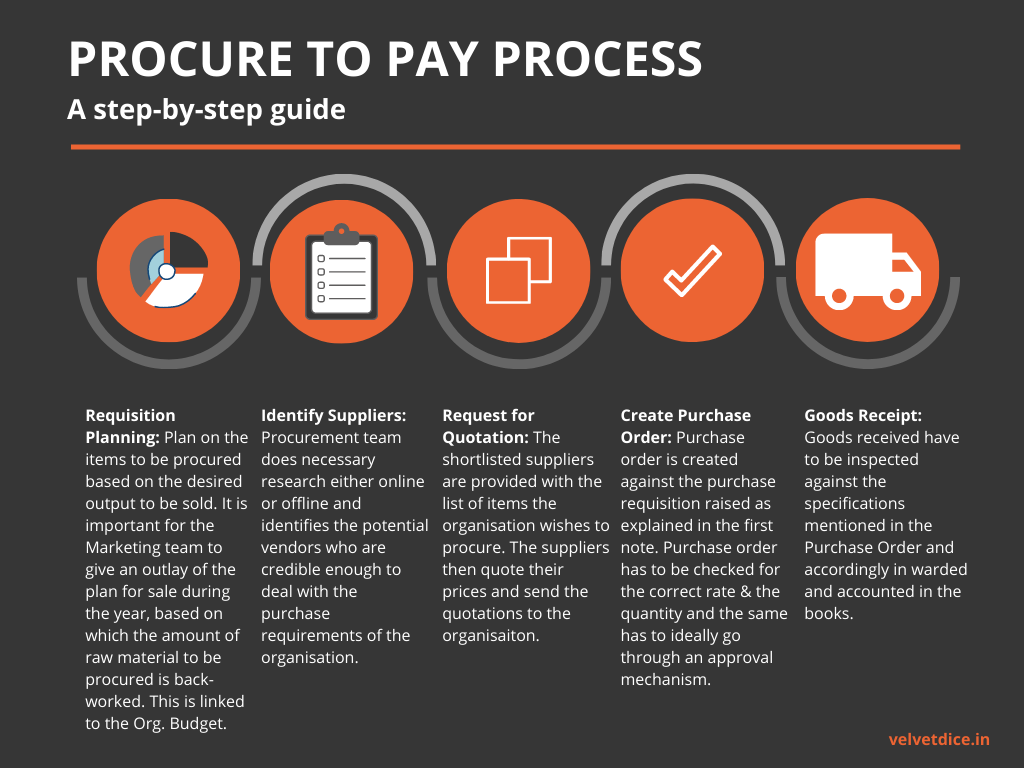

Audit has to be planned in such a fashion that the key risks that were identified at the time of process walkthrough are addressed in one or the other way. In a few organizations the data that is maintained usually lacks the necessary fields to perform analytics or pick samples for verification. It is important to understand every field that is available in the data received, in order to assess if there’s possibility of manipulating the IT system to the favor of the personnel operating that process in the organization.
Despite the availability of technology that can drastically reduce the man-hours spent in collating and analysing the P2P data and inefficiencies plaguing accounts payable, few companies have addressed account payable transformation like other processes essential to the business while others still use the approach of manual transaction monitoring.
Following are the key analytics indicators:

Read about how to identify duplicate invoices by clicking here.
This P2P guide has been divided into the following key sub-processes within the Procure to Pay business cycle:
- Procurement Planning
- Vendor Selection
- Requisitioning and Ordering
- Receipt of goods and services
- Invoice Processing
- Accounts Payable
- Vendor Performance Assessment
We will discuss each sub-processes in the following articles with real world practical examples.
What should organisations do to address this ?
You can employ automated and repeatable analytics for immediate fraud detection plus manage and track anomalies from initial detection to resolution. With automated monitoring, Business Process Owners are able to reap significant cost savings by identifying and resolving issues at source, rather than during periodic audits. The organisation also gets the added intelligence of identifying root causes that can now be addressed to help with overall improvement of the procurement process.
Thanks for reading! Until next time.


Good intro & concept flow to the topic.